Topic: DAX
-
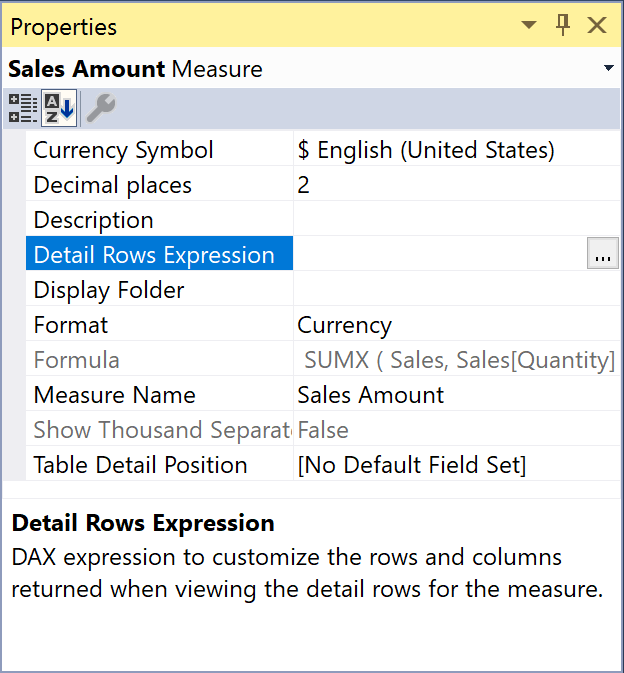
The Detail Rows Expression in a Tabular model provides the user with control over the drillthrough results obtained by showing details of a measure. This article describes typical DAX expressions you can use in this property. Read more
-
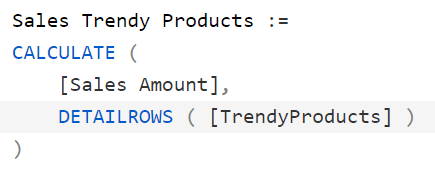
This article describes how to use the detail rows expression of a measure to obtain the equivalent of creating table functions in DAX. This allows the reusing of a table expression in multiple CALCULATE filters. Read more
-
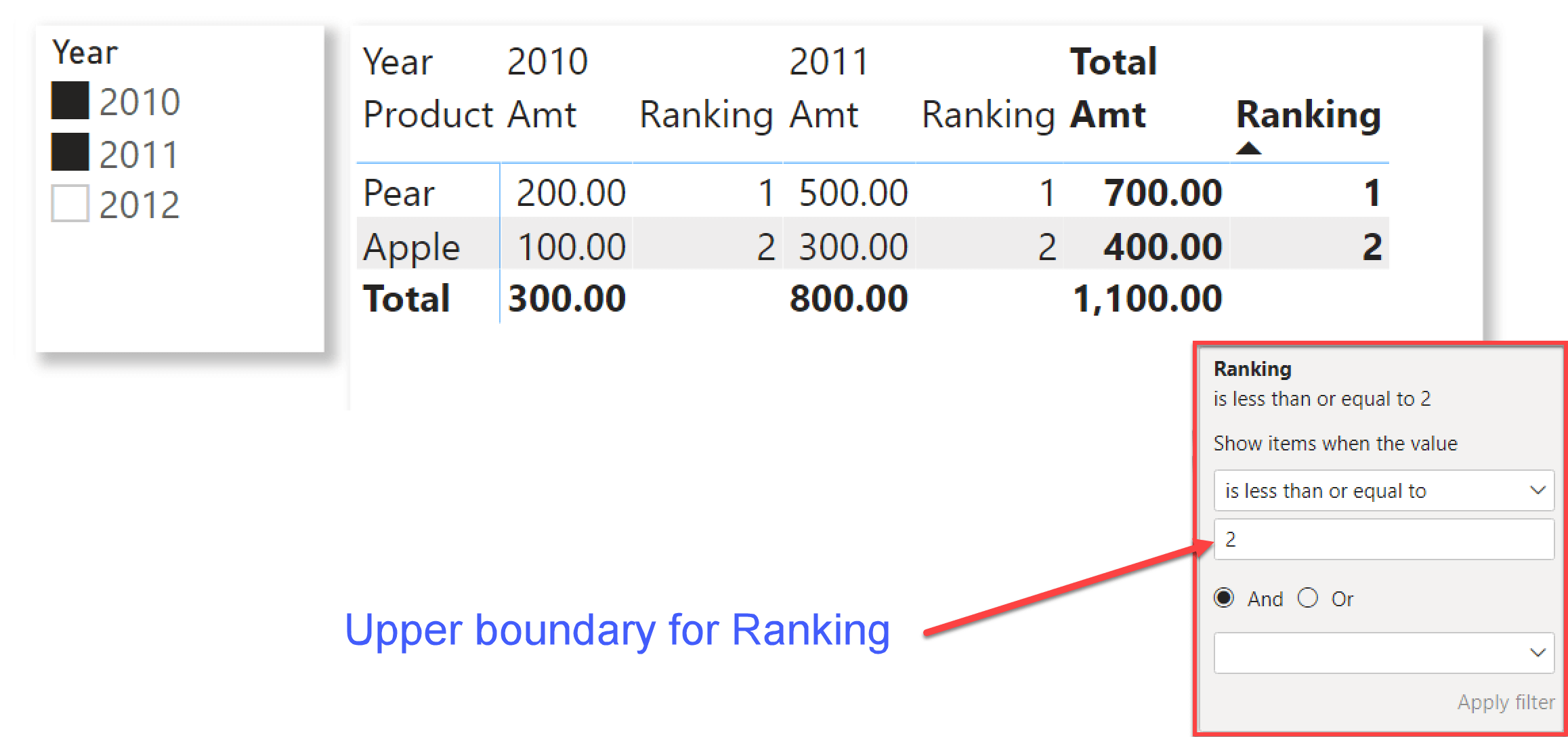
When you use a measure as a filter in a Power BI visual, the DAX code generated might display different behaviors depending on whether the measure is part of the values shown in the visual or not. In this article,… Read more
-
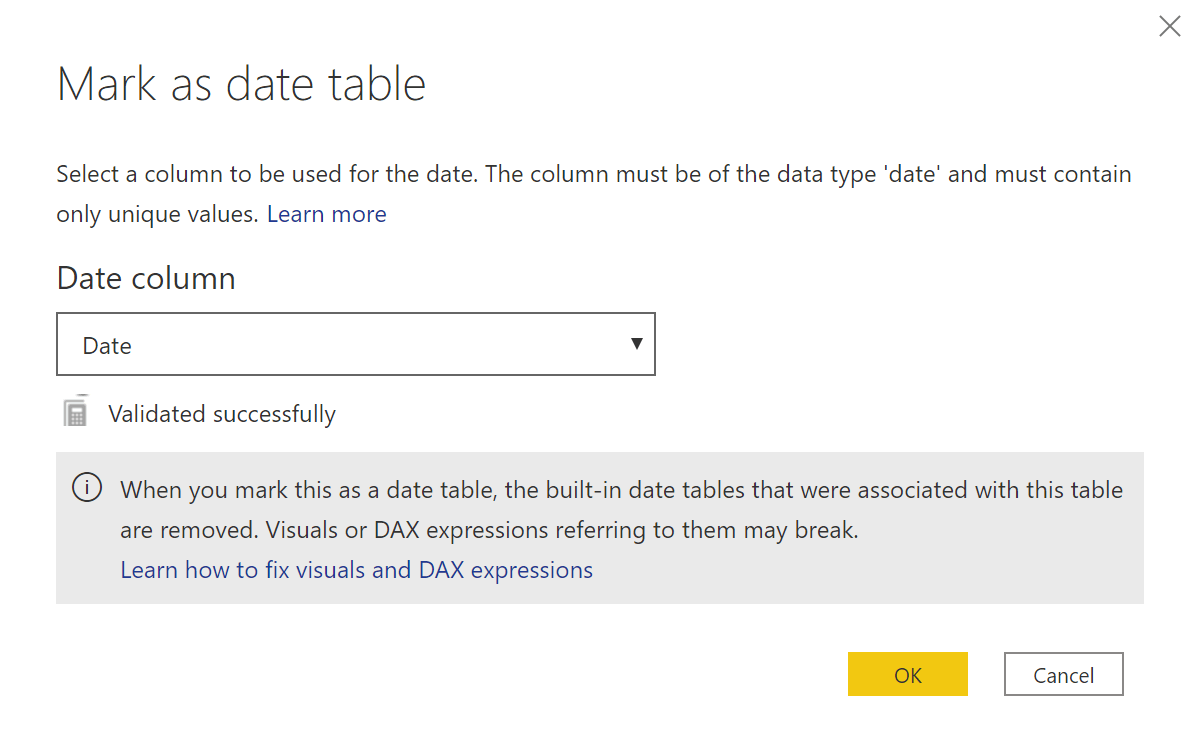
Tabular models (including Power BI) require marking the Date table as a date table to get appropriate results with time intelligence calculations. This article explains why this setting is required. Read more
-
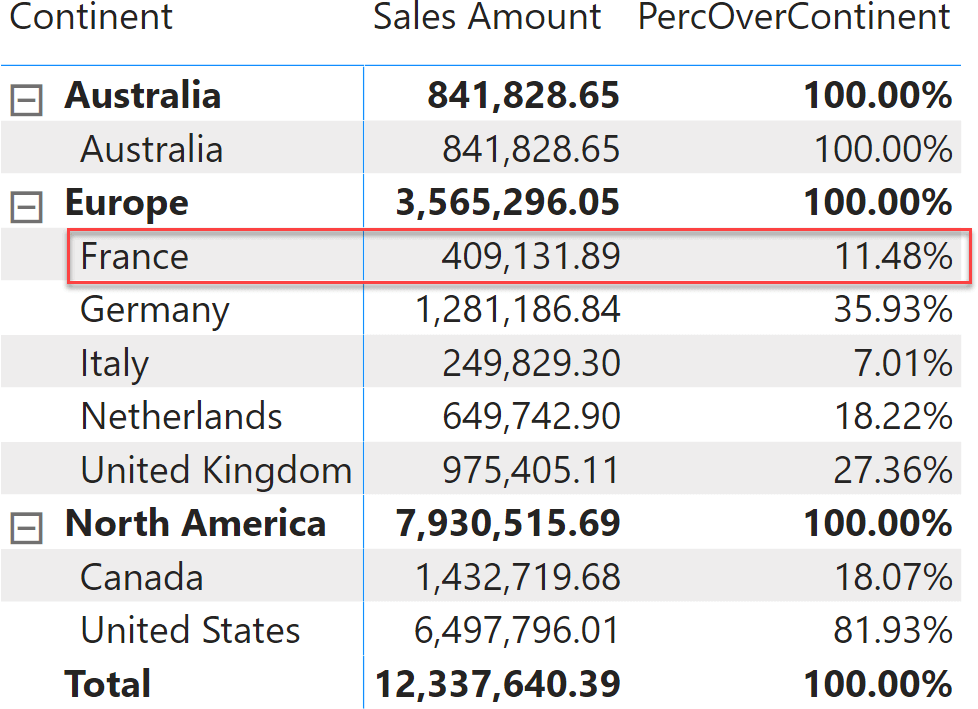
ALLEXCEPT is a handy DAX function to retrieve all the columns of a table except for some. When used as a CALCULATE modifier, its behavior is less intuitive and might result in inaccurate measures. In this article, we elaborate on… Read more
-
This article describes the semantic difference between ALLEXCEPT and the joint use of ALL and VALUES, showing practical examples of the different results in Power BI and SSAS 2016. Read more
-
This article explains how the CONTAINS function works and what can be used as better alternatives in DAX in common use cases. Read more
-
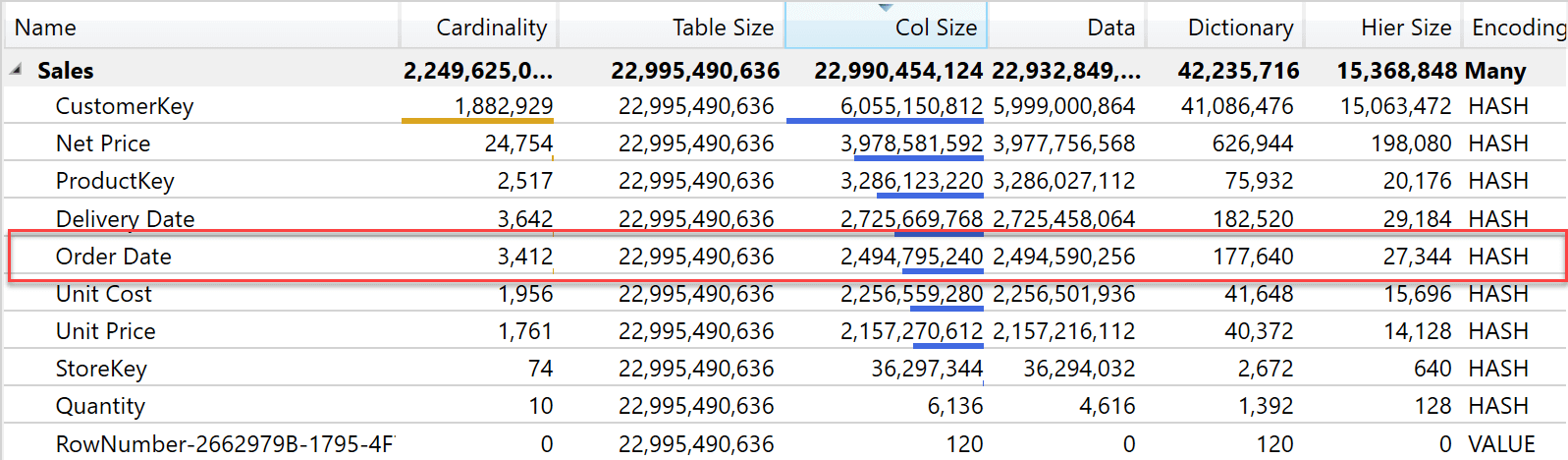
This article provides you with the technical knowledge to choose between using a Date or an Integer to create the relationship between your fact table and the Date dimension. Read more
-
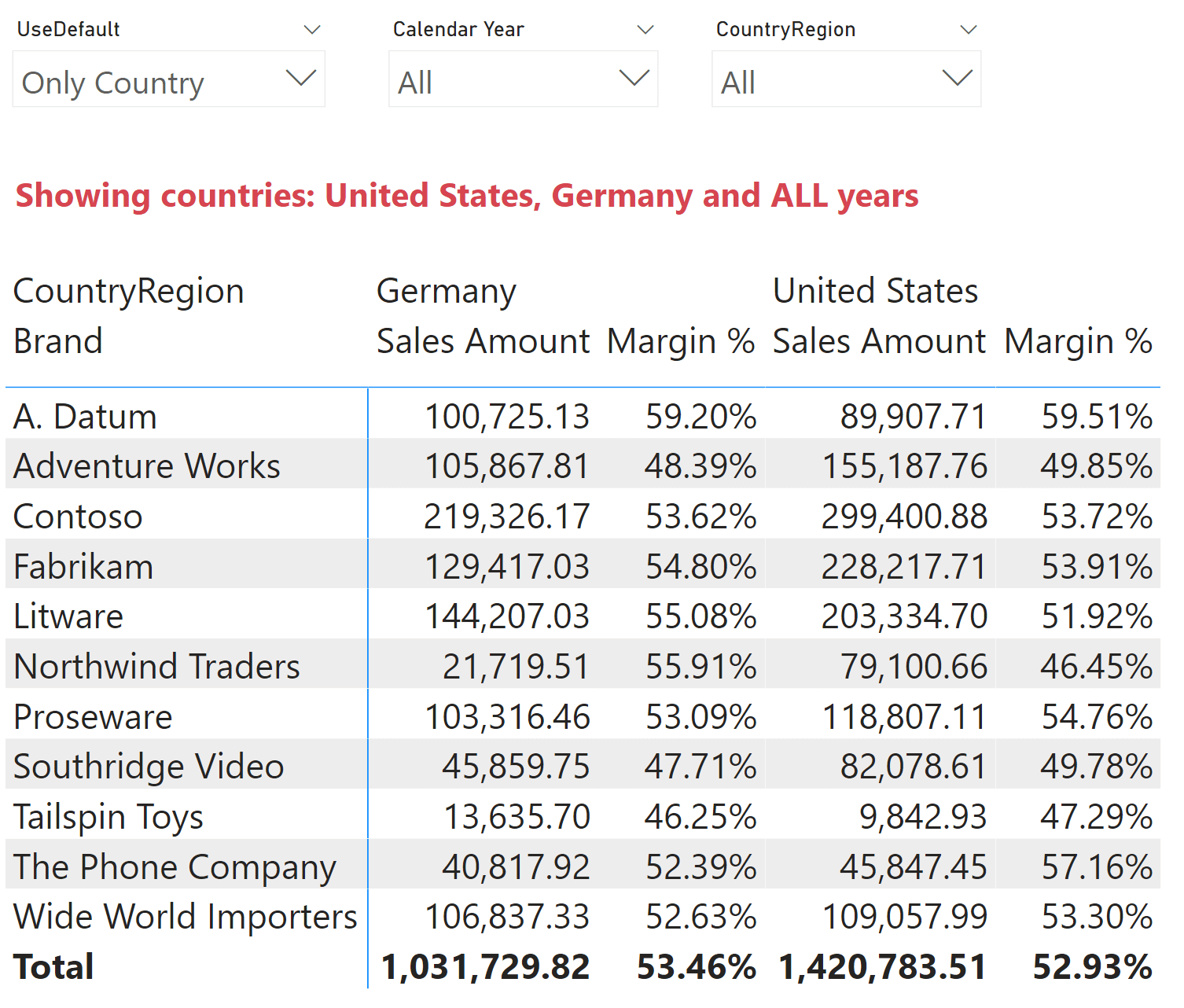
This article shows how to use calculation groups to define a default set of values for columns in your model. Different users can have different default values, and yet retain the full capability to select different values. Read more
-
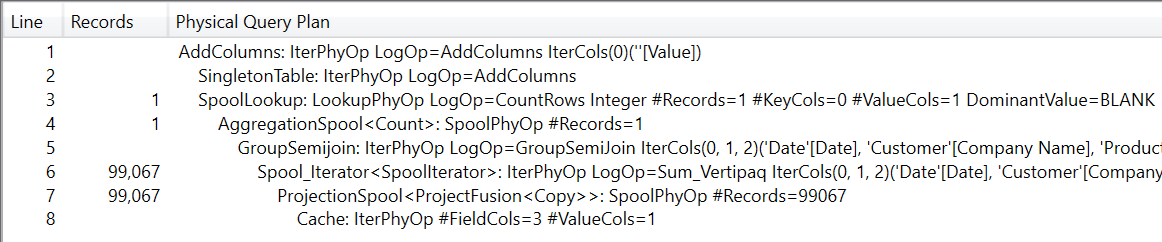
This article describes how blank values considered in a DAX conditional expression can affect its query plan and how to apply possible optimizations to improve performance in these cases. Read more