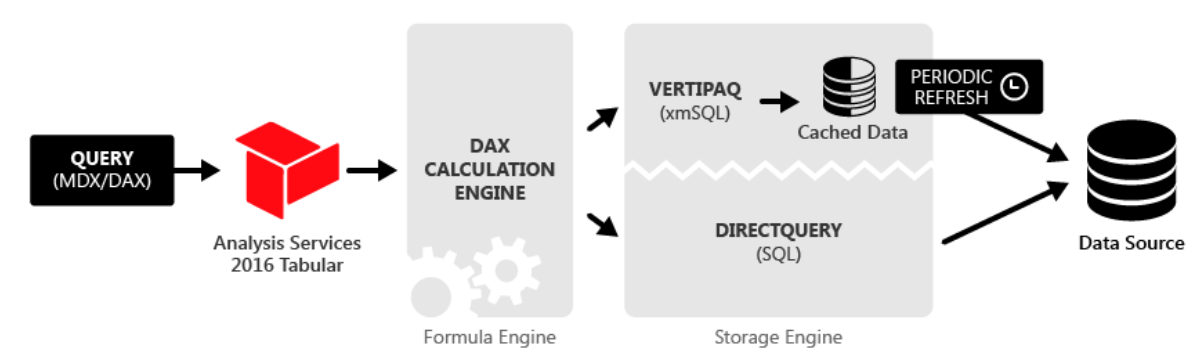
Topic: Tabular
-
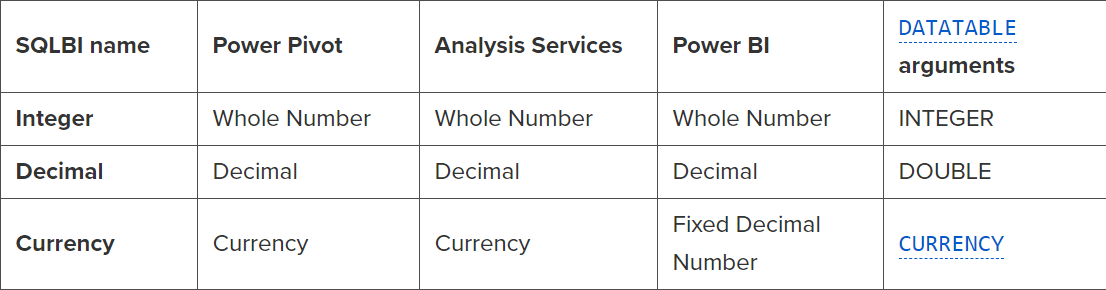
This article describes how DAX automatically converts data types in arithmetic operations. These small details can cause and explain differences in results when using the same operations in other languages. Read more
-
ALLSELECTED is a powerful function that can hide several traps. This article is an in-depth analysis of the behavior of ALLSELECTED, explaining shadow filter contexts, what they are and how they are used by ALLSELECTED. Read more
-
This article describes how to use variables to optimize the performance of DAX expressions containing multiple instances of the same measure or the same sub-expression. Read more
-
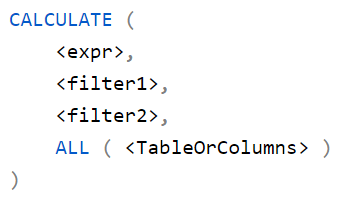
This article explains how the context transition interacts with the filter arguments of a CALCULATE function in DAX. This is important in order to avoid unexpected results with complex calculations made in filter arguments. Read more
-
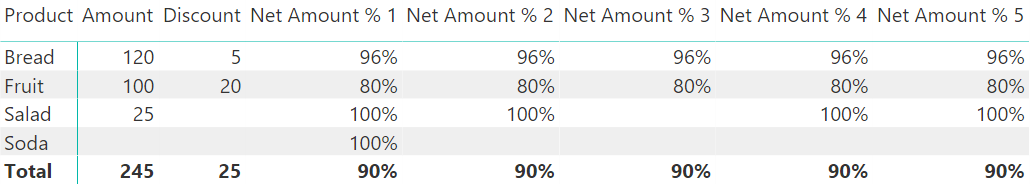
This article describes a counterintuitive behavior of BLANK in DAX measures affecting Power BI, Analysis Services, and Power Pivot. That behavior could cause mistakes in a report using alternate expressions of the same calculation. Indeed, these expressions are not equivalent… Read more
-
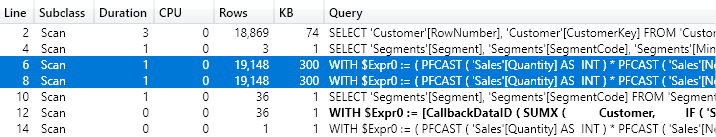
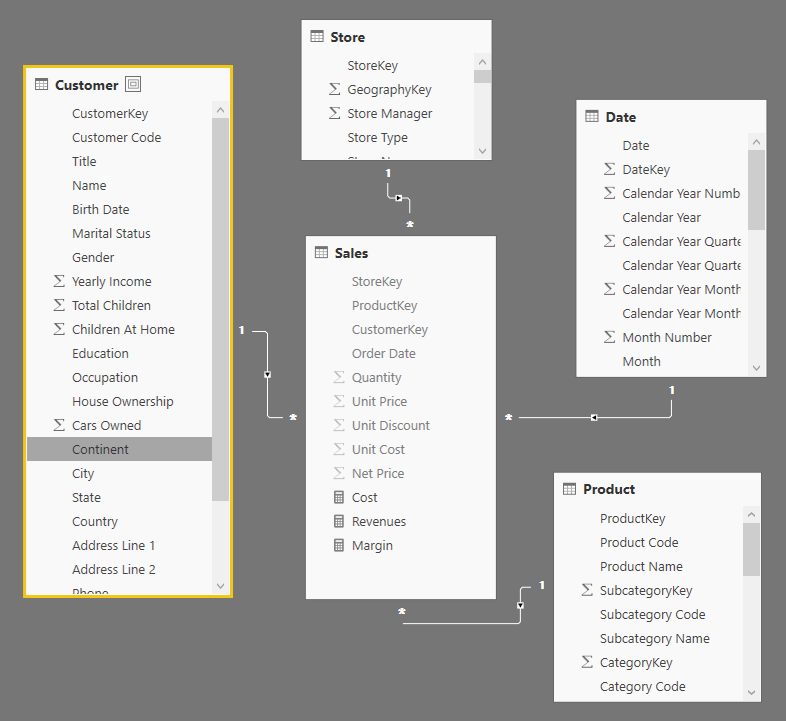
This article describes how to extract raw data stored in the Tabular engine, used by Analysis Service Tabular, Power BI, and Power Pivot. Read more
-
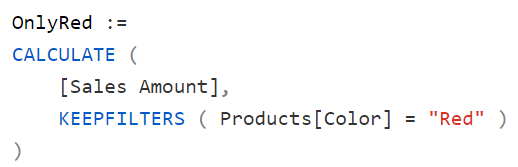
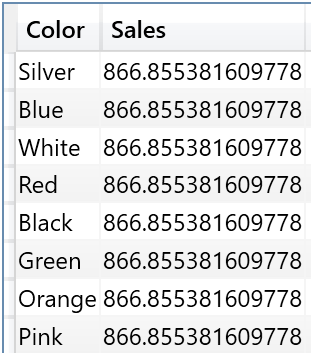
This article explains how to use KEEPFILTERS to intersect instead of overriding an existing filter context in DAX, simplifying the code and improving performance. Read more
-
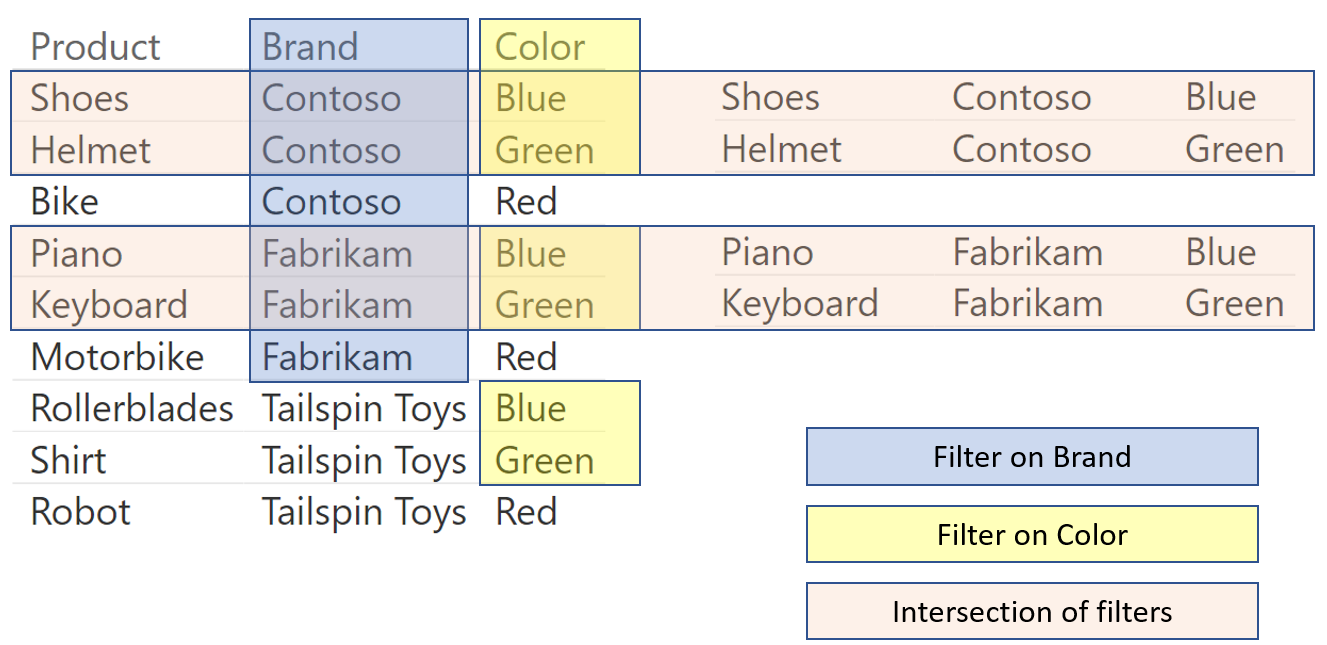
This article describes how table expansion and filter context propagation are important DAX concepts to understand and fix small glitches in DAX expressions. Read more
-
This article describes how to implement non-visual-totals with security roles in Power BI and Analysis Services Tabular, which by default show only visual totals of measures in the model. Read more
-
This article describes a few query limits existing in DirectQuery for both Power BI and Analysis Services Tabular 2016, explaining when you can modify them. Read more