Topic: Filter Context
-
This article describes how to create a virtual relationship in DAX using the TREATAS function, which is more efficient than approaches based on INTERSECT or FILTER. Read more
-
RELATED and its companion function RELATEDTABLE, are two common DAX functions that are required when using a row context with relationships. In this article we describe why and when to use these two functions. Read more
-
This article explains how to use KEEPFILTERS to intersect instead of override an existing filter context in DAX. Using KEEPFILTERS simplifies the code and improves performance. Read more
-
Context transition is one of the most obscure topics for DAX newbies. In this article we introduce context transition, its effects, and how to leverage it rather than be scared of it. Read more
-
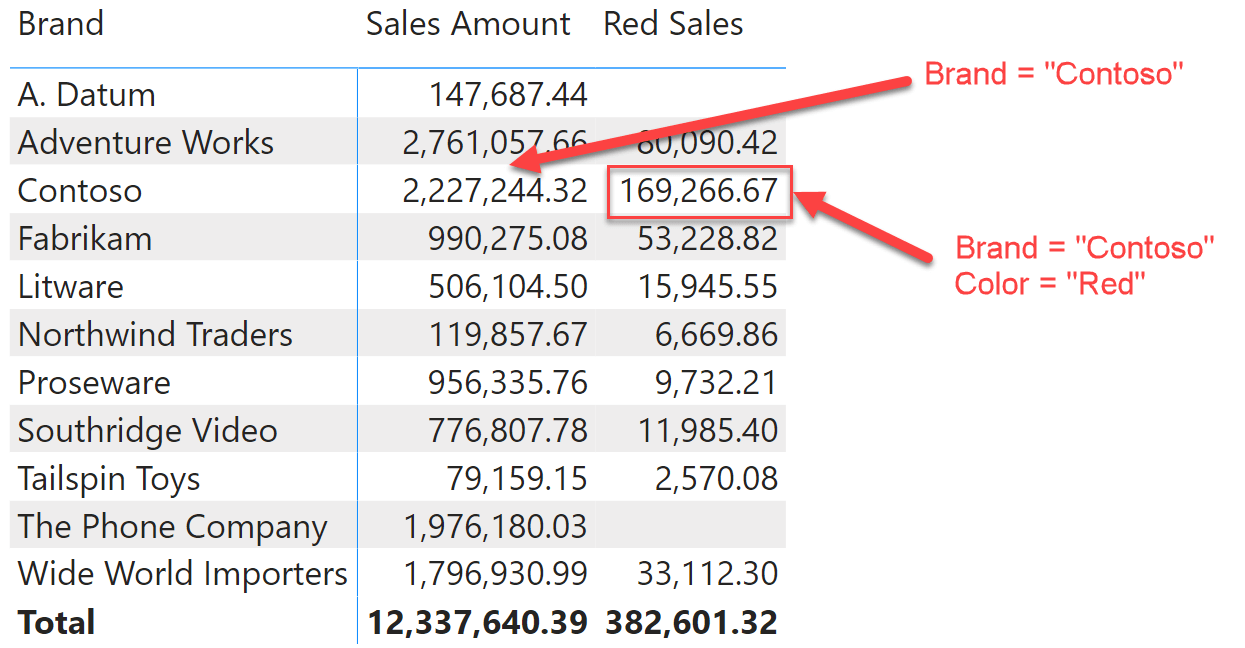
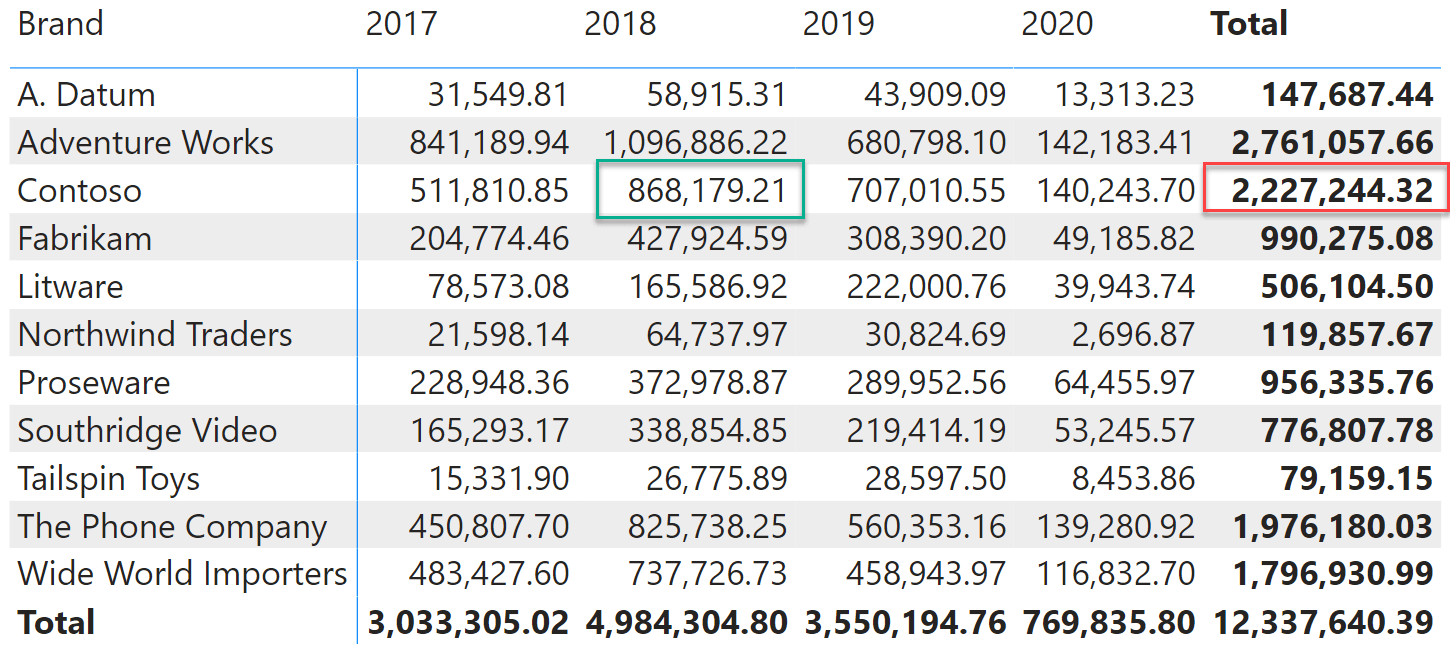
CALCULATE is the most powerful and complex function in DAX. In this article, we provide an introduction to CALCULATE, its behavior, and how to use it. Read more
-
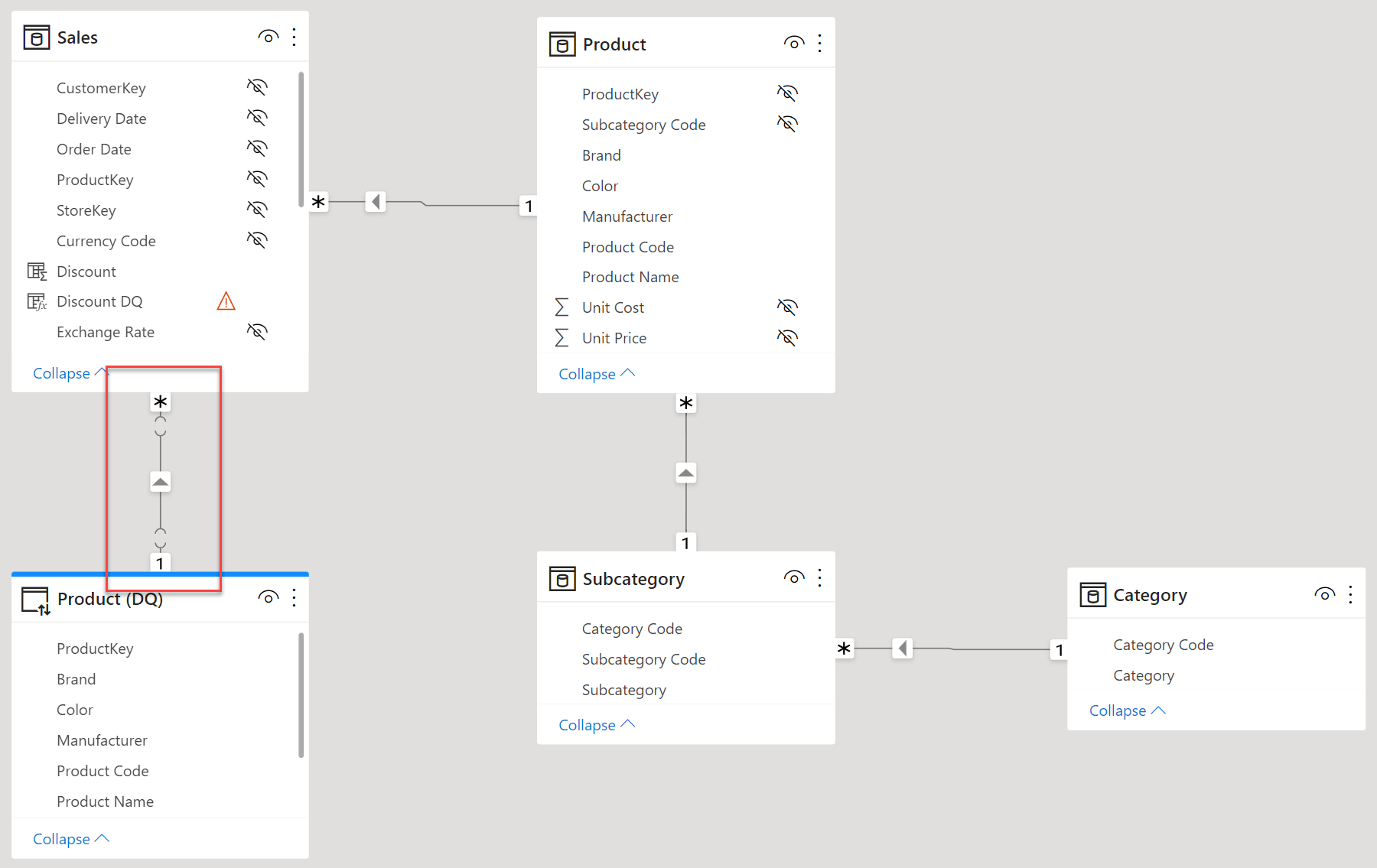
Understanding the difference between a row context and a filter context is the first and most important concept to learn to use DAX correctly. This article introduces the filter context. Read more
-
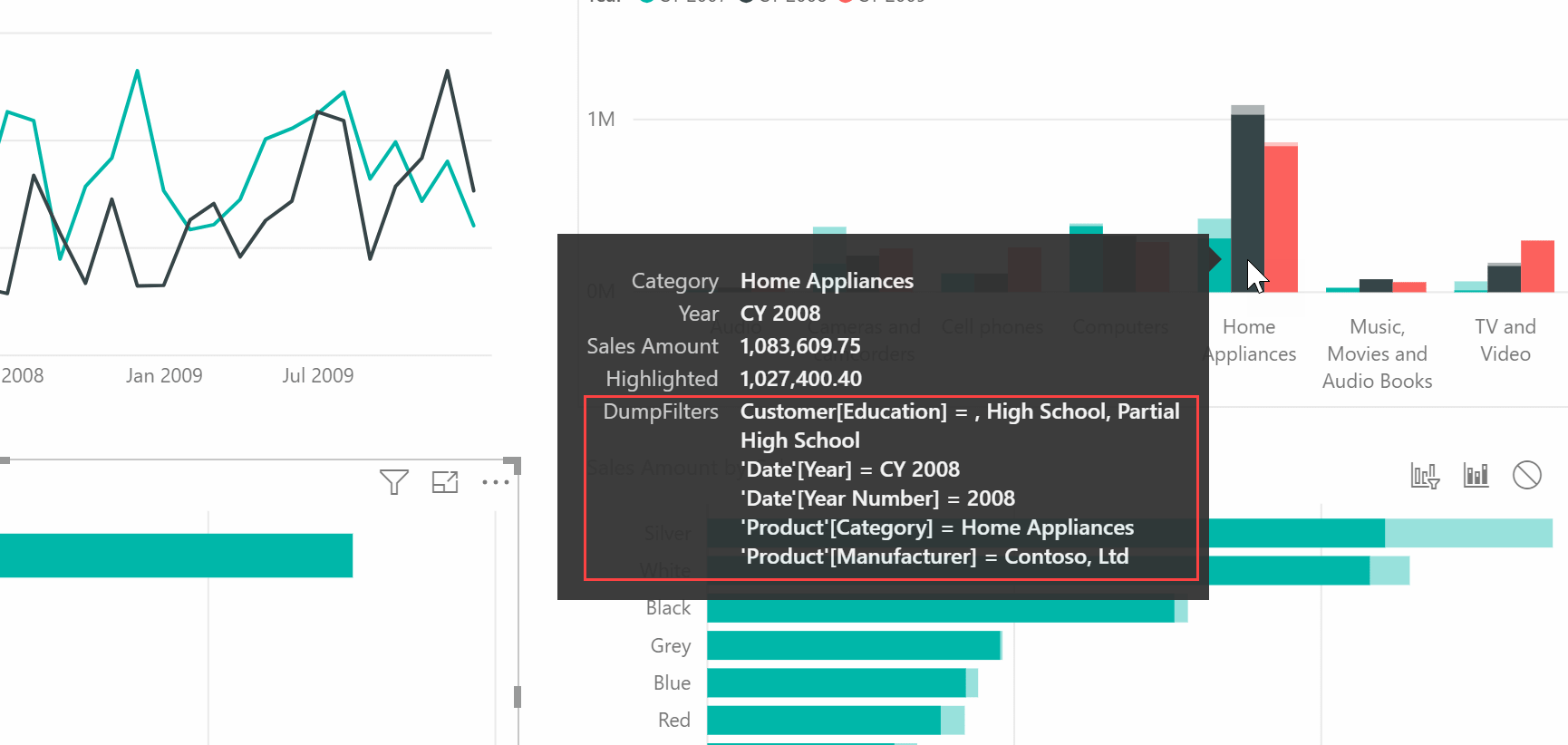
This article describes how to display the filter context applied to a calculation using a special DAX measure in Power BI Tooltips. Read more
-
SUMMARIZE is a very powerful and very complex function to use. This article describes its internal behavior, and provides guidance on how to use it. Read more
-
In Power BI Desktop (as of February 2016) you have to use DAX to apply calculations over dates (such as year-to-date, year-over-year, and others), but you do not have the Mark as Date Table feature. This article describes which scenarios… Read more
-
This article provides a complete explanation of the behavior of the ALLxxx functions in DAX. When used as filters in CALCULATE, ALLxxx functions might display unexpected behaviors. Read more