Topic: DAX
-
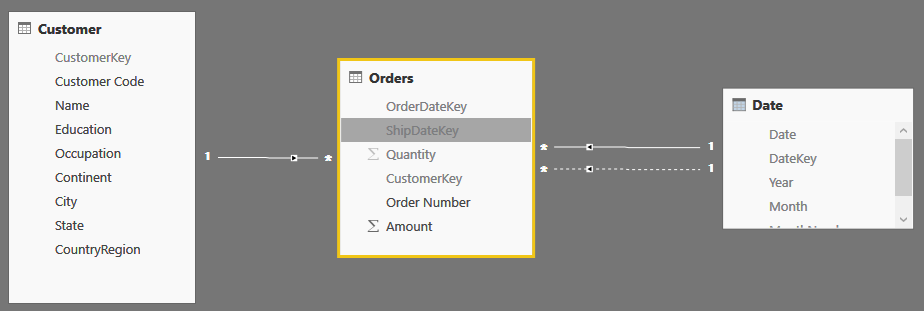
This article analyzes how to efficiently work with events that lasts over time, such as the duration of an order considering the distance between order date and ship date. Read more
-
In this article, Alberto Ferrari describes a new efficient way to compute returning customers in DAX thanks to an idea suggested by a student attending an Optimizing DAX workshop. Read more
-
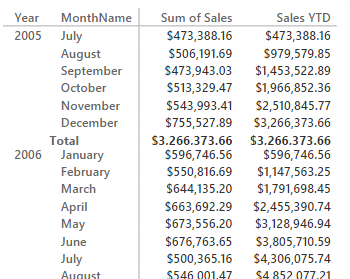
In Power BI Desktop (as of February 2016) you have to use DAX to apply calculations over dates (such as year-to-date, year-over-year, and others), but you do not have the Mark as Date Table feature. This article describes which scenarios… Read more
-
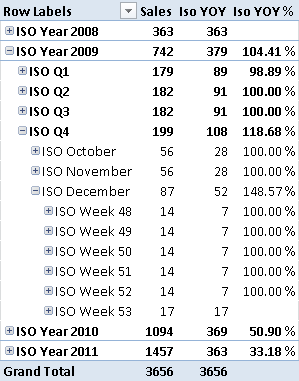
This article describes how to implement a custom year-over-year calculation in DAX based on arbitrary associations between different periods. As an example, we describe the comparison of the 53rd week in a ISO Calendar. Read more
-
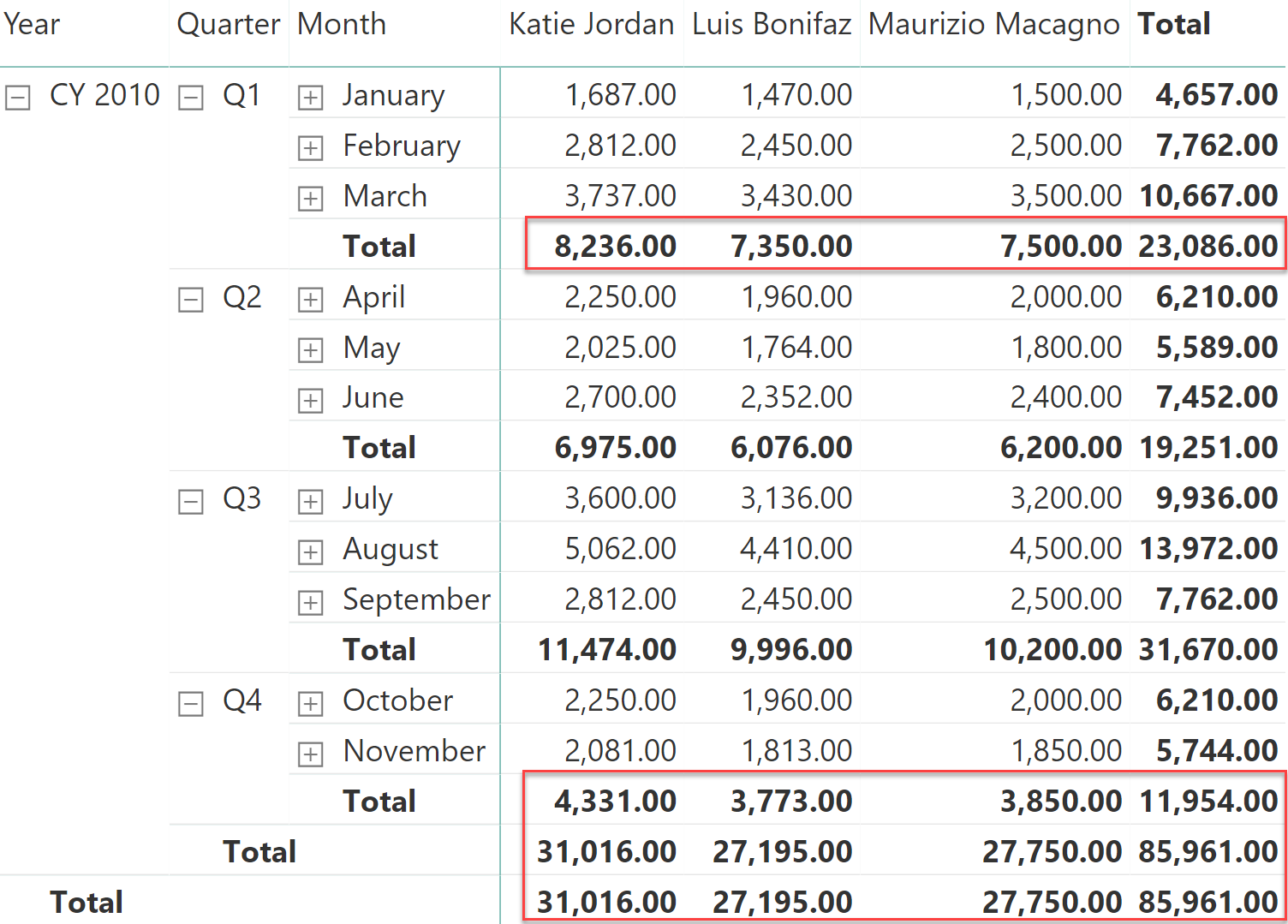
Values such as inventory and account balance, usually calculated from a snapshot table, require the use of semi-additive measures. This article describes how to implement these calculations in DAX according to your specific requirements. Read more
-
Values such as inventory and balance account, usually calculated from a snapshot table, require the use of semi-additive measures. In Multidimensional you have specific aggregation types, like LastChild and LastNonEmpty. In PowerPivot and Tabular you use DAX, which is flexible… Read more
-
This article shows a technique in DAX to compute the sales volume of products that were available right from the beginning of a selected time period, ignoring products introduced afterwards. Read more
-
This article describes how to implement a syntax equivalent to the T-SQL function NULLIF and the ANSI SQL function COALESCE, in DAX. Read more
-
This article describes the reasons why an Excel pivot table may be slow when using the Analyze in Excel feature of Power BI. Read more
-
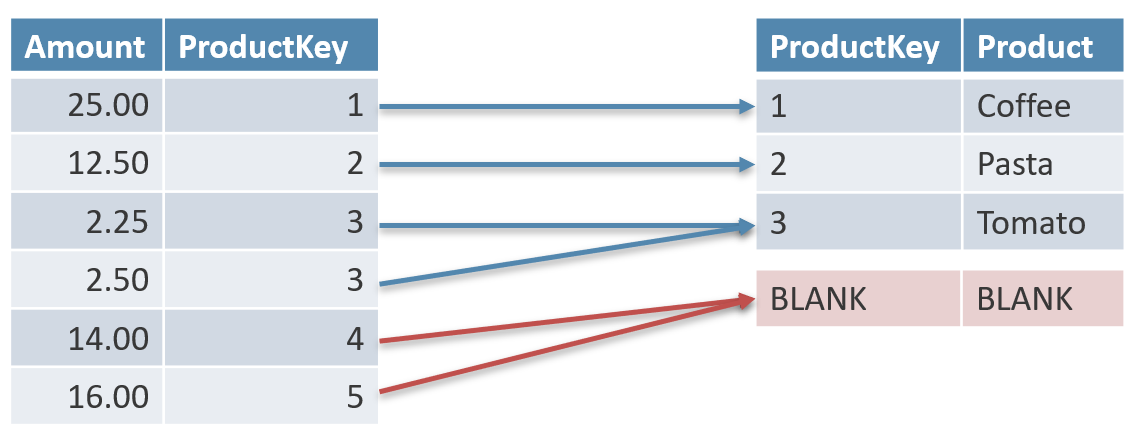
There are two functions in DAX that return the list of values of a column: VALUES and DISTINCT. This article describes the difference between the two, explaining the details of the blank row added to tables for invalid relationships. Read more