Topic: DAX
-
The GROUP BY condition of a SQL statement is natively implemented by SUMMARIZE in DAX. This article shows how to use SUMMARIZE and an alternative syntax to group data. Read more
-
The WHERE condition of an SQL statement has two counterparts in DAX: FILTER and CALCULATETABLE. In this article we explore the differences between them, providing a few best practices in their use. Read more
-
The DIVIDE function in DAX is usually faster to avoid division-by-zero errors than the simple division operator. However, there are exceptions to this rule, described in this article through a simple performance analysis. Read more
-
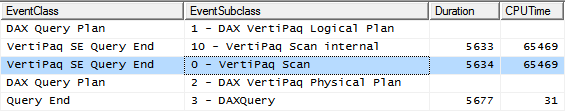
In DAX there are different ways to test whether a table is empty. This test can be used in complex DAX expressions and this short article briefly discuss what are the suggested approaches from a performance perspective. Read more
-
A common best practice is to use CALCULATETABLE instead of FILTER for performance reasons. This article explores the reasons why and explains when FILTER might be better than CALCULATETABLE. Read more
-
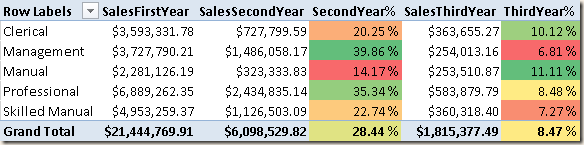
With DAX you can calculate the sales of the first, second and third year of a new customer without any ETL. In this article you see how to implement this calculation with good performance. Read more
-
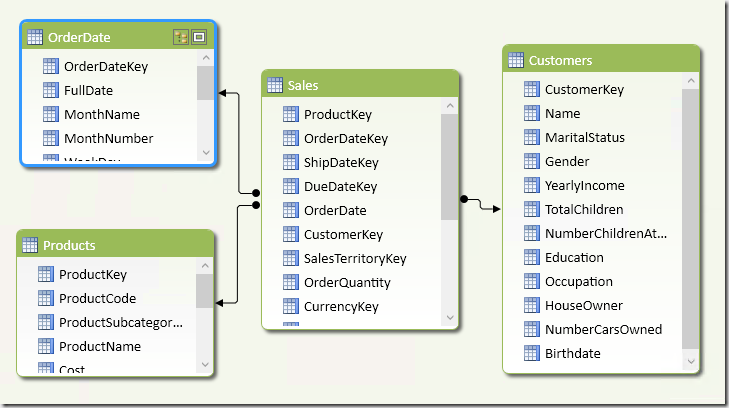
Grouping transactions by customers’ age requires a computation made row by row at transaction level. DAX offers an elegant solution using calculated columns, which is described in this article. Read more
-
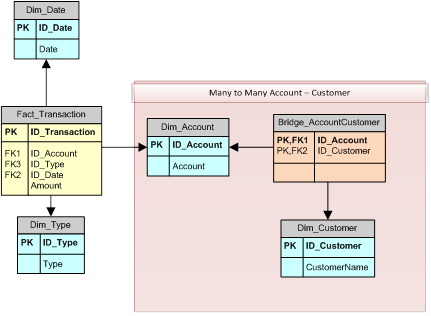
PowerPivot and Analysis Services 2012 Tabular do not support many-to-many (M2M) relationships directly in the data model. However, you can obtain the desired result from a many-to-many relationship by writing a DAX expression. For example, consider the classic M2M relationship… Read more
-
DAX is the new language used by PowerPivot and Analysis Services in Tabular mode and it resembles the syntax of Excel formula and it can be considered a functional language. You do not have iterative statements, but you can run… Read more
-
In DAX string comparison requires you more attention than in SQL, for several reasons: DAX doesn’t offer the same set of features you have in SQL, a few text comparison functions in DAX are only case-sensitive and others only case-insensitive,… Read more