Topic: Tabular
-
This article explains how to improve DAX queries using GENERATE and ROW instead of ADDCOLUMNS when you create table expressions. Read more
-
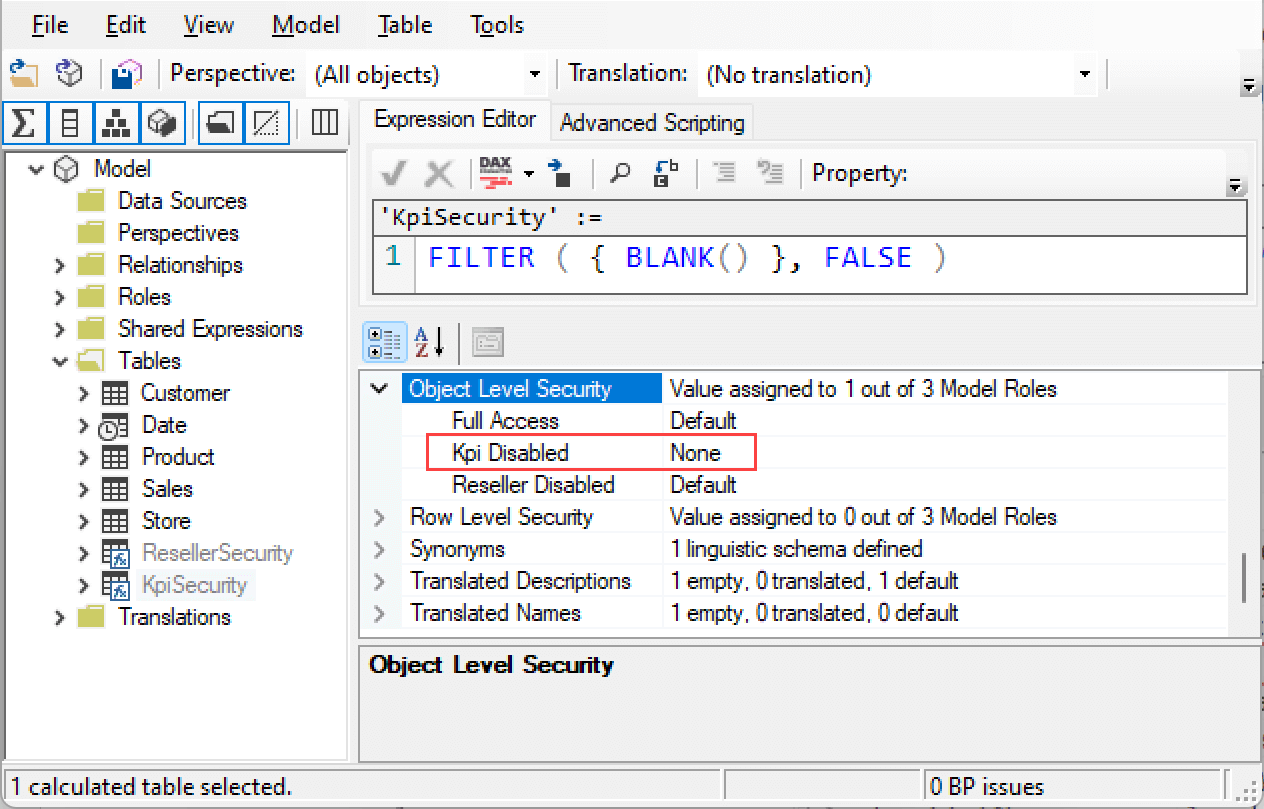
This article describes how to hide measures from a group of users by leveraging object-level security in Power BI and Analysis Services. Read more
-
One of the first concepts to learn in DAX is the difference between calculated columns and measures. This article shortly recaps the differences and describes when to use each one. Read more
-
Using ALLSELECTED with no arguments in a remote model later used in a composite model might produce unexpected results. In this article we examine the topic and provide the reasons why ALLSELECTED requires special attention. Read more
-
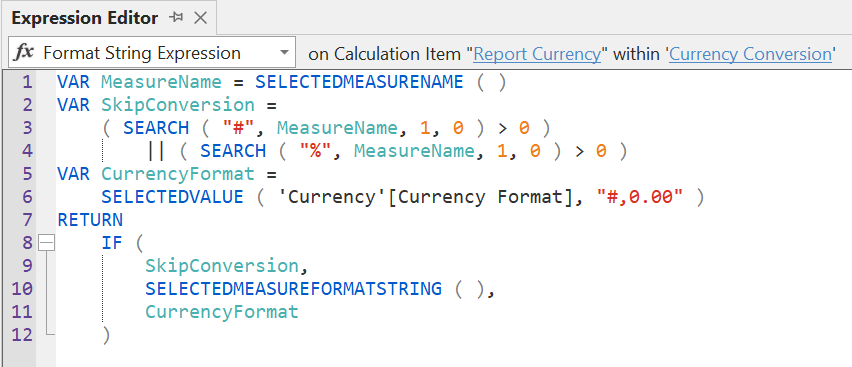
This article introduces the syntax to describe in a textual form the DAX expressions and additional properties of calculation groups. Read more
-
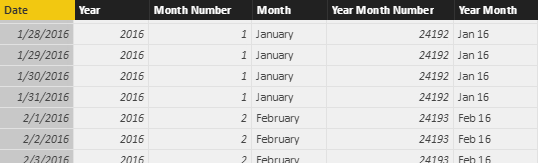
This article explains how to use SUMMARIZECOLUMNS, which is a replacement of SUMMARIZE and does not require the use of ADDCOLUMNS to obtain good performance. Read more
-
When used in a composite model, calculation groups show a very unique behavior that a good DAX developer must understand well to build sound models. In this article we describe how composite models and calculation groups work together. Read more
-
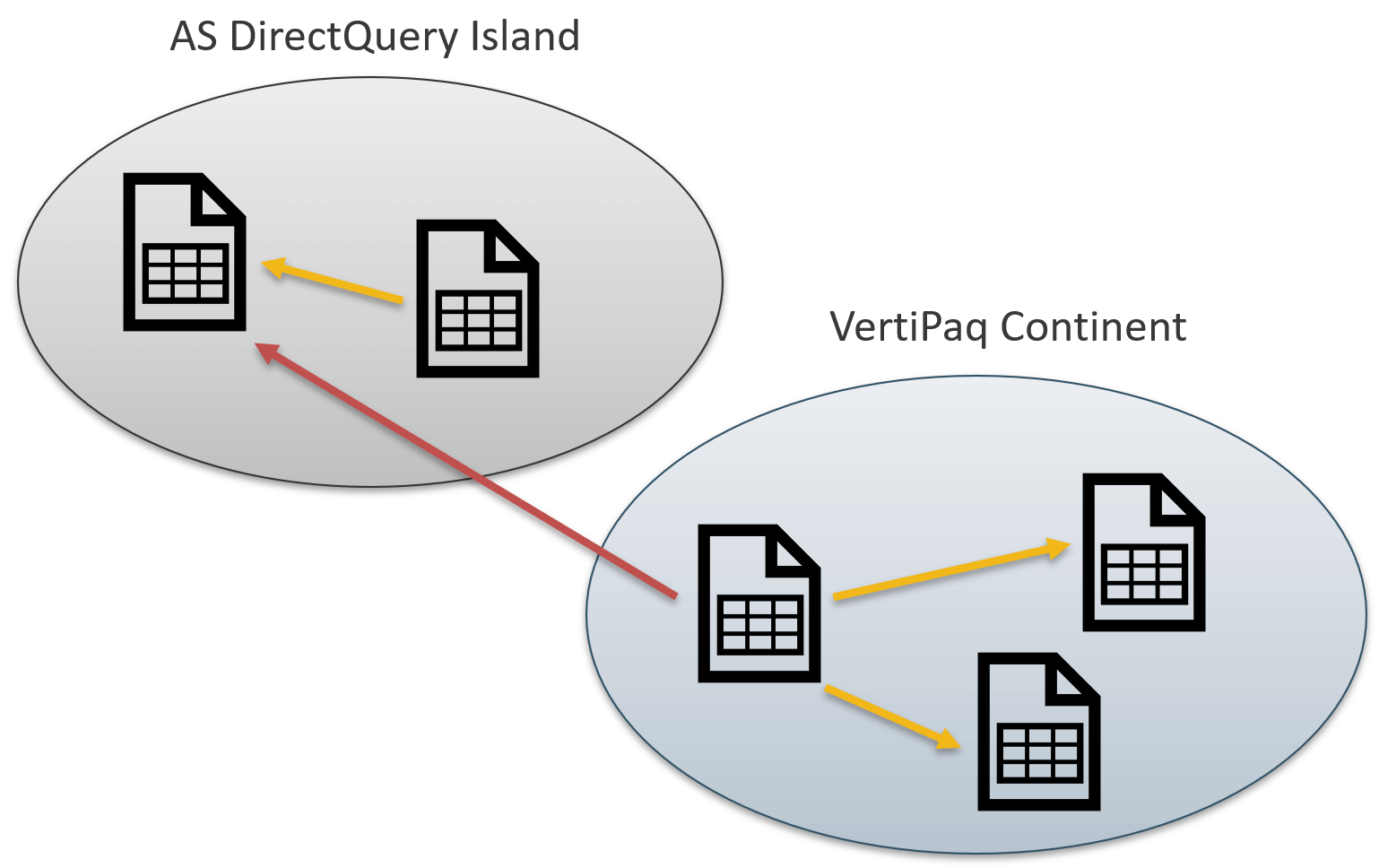
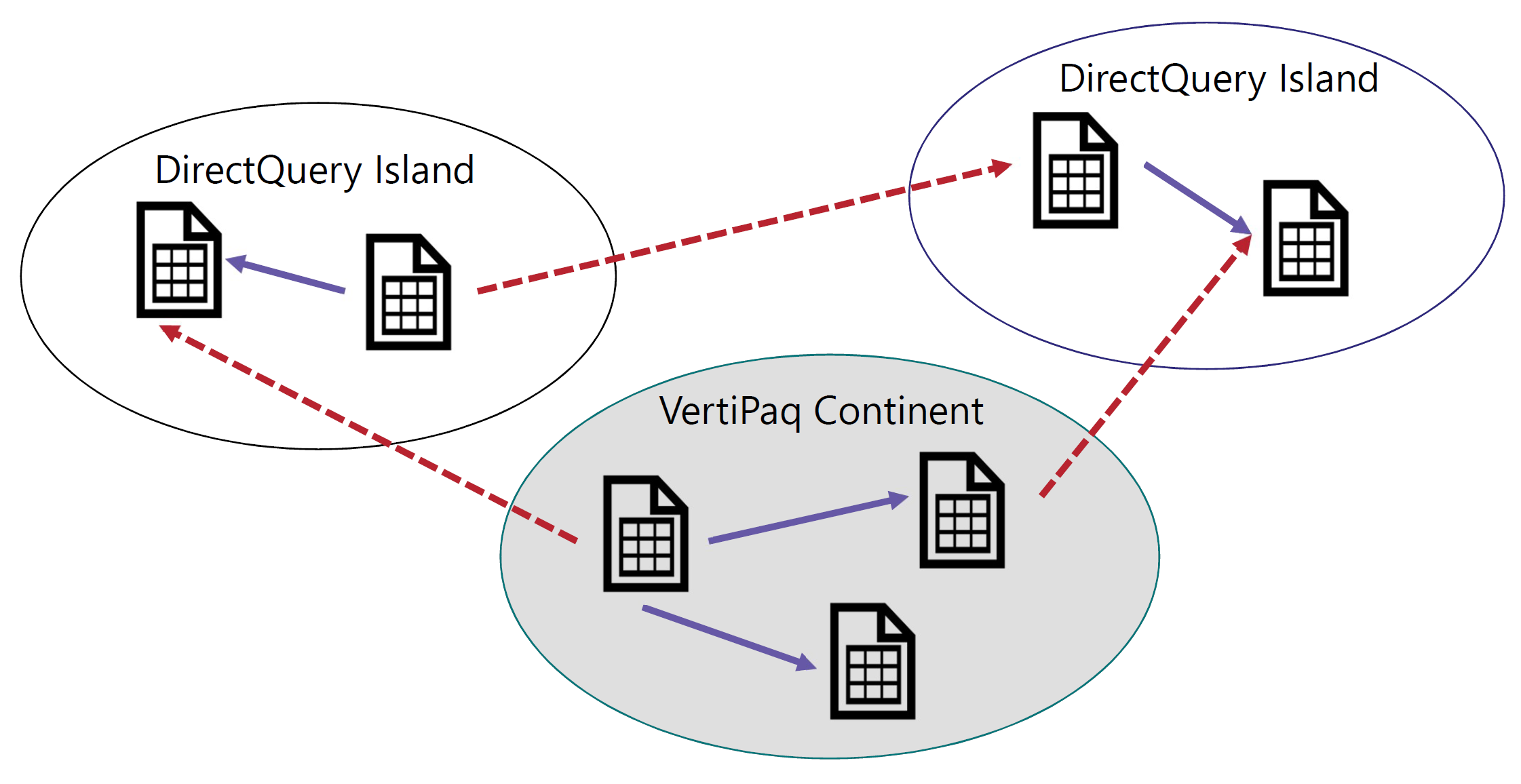
In composite models, any query can be executed on the remote model (wholesale execution) or by mixing local and remote engines together (retail execution). This article describes the differences between the wholesale and retail modes, along with examples. Read more
-
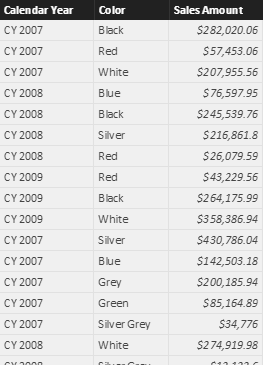
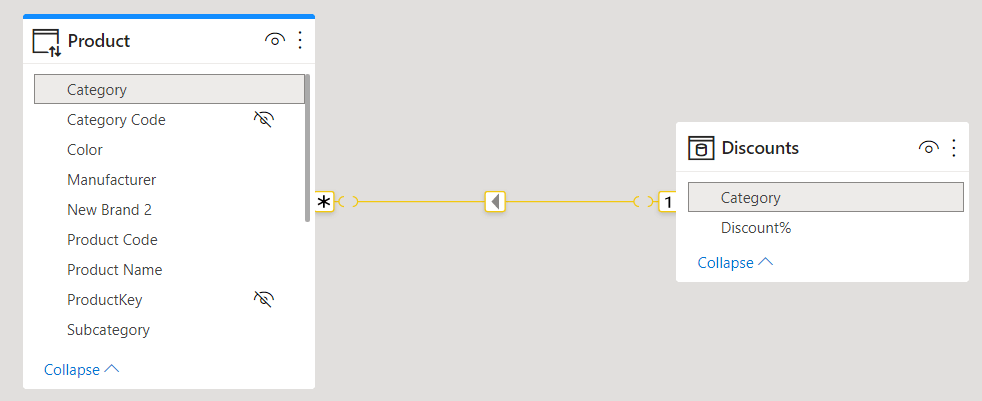
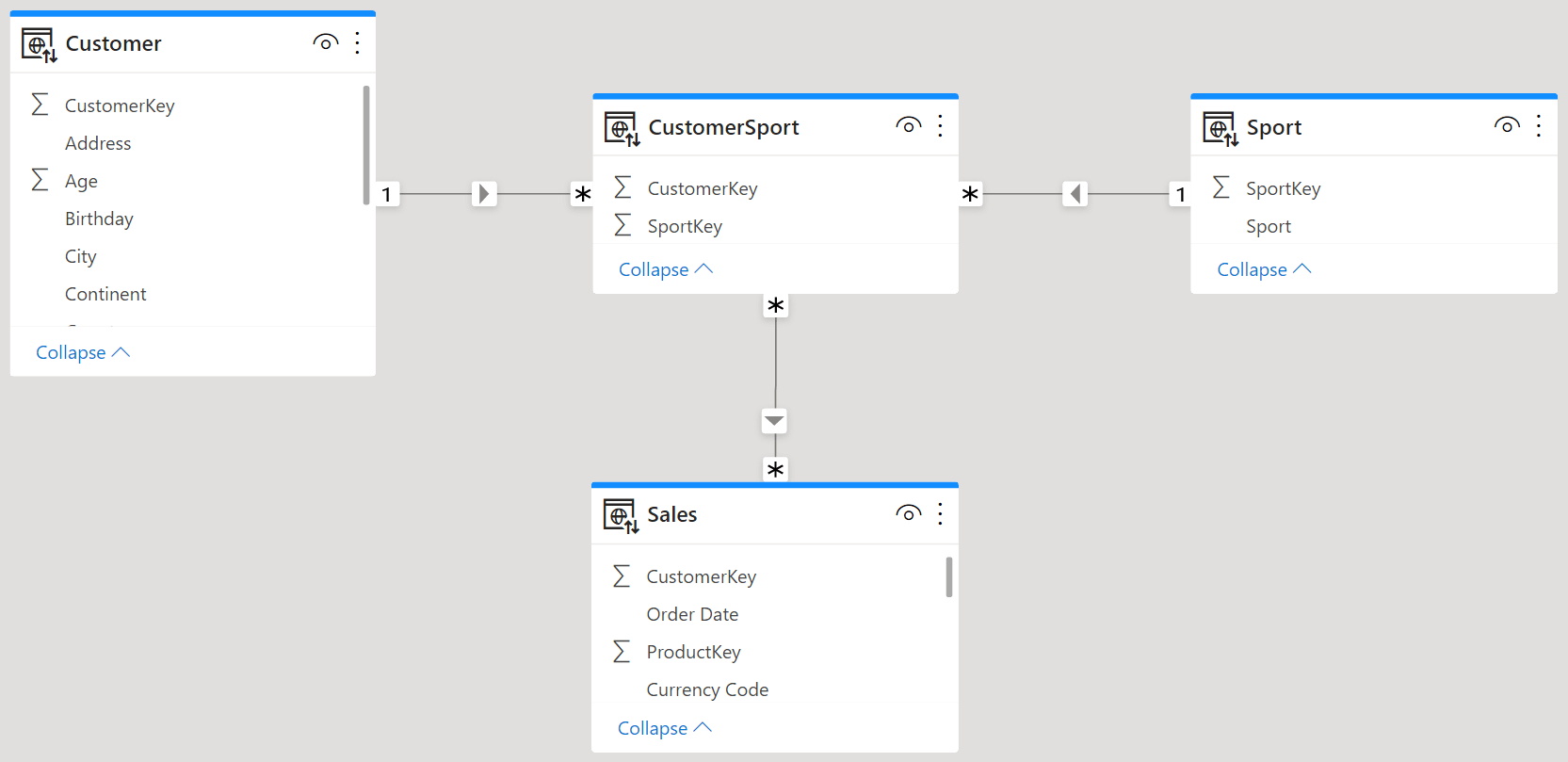
There are two options to model many-to-many relationships using Tabular and Power BI: you can use either a regular bidirectional filter relationship, or a limited unidirectional relationship. In this article, we compare the performance of both options. Read more
-
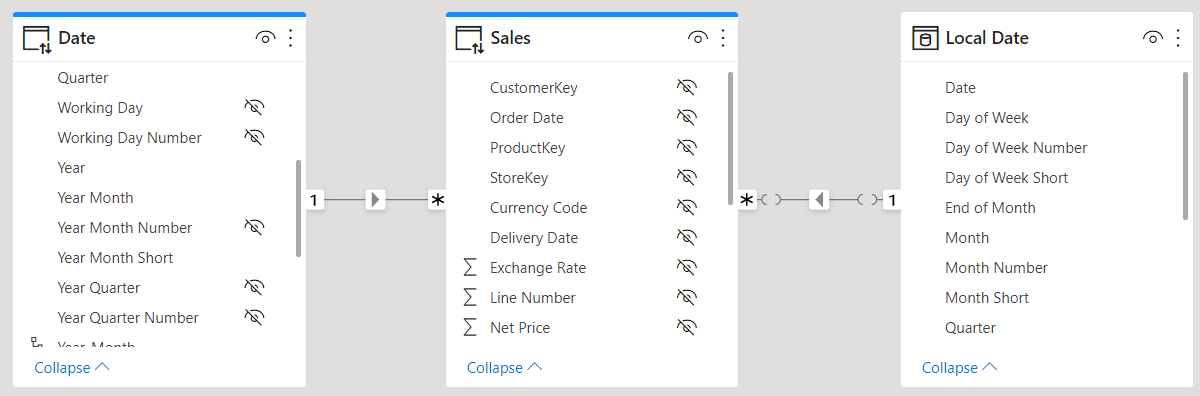
This article describes the types of relationships available in Power BI and Analysis Services, clarifying the differences in cardinality and filter propagation of physical relationships. Read more